TigerVNC is a free, open-source and high-performance VNC server used to control or access Linux based desktop systems remotely. It is a client/server application that allows you to interact with graphical applications on remote machines. This tutorial described you to how to install and configure VNC server on Ubuntu 18.04 Linux system..
Prerequisites
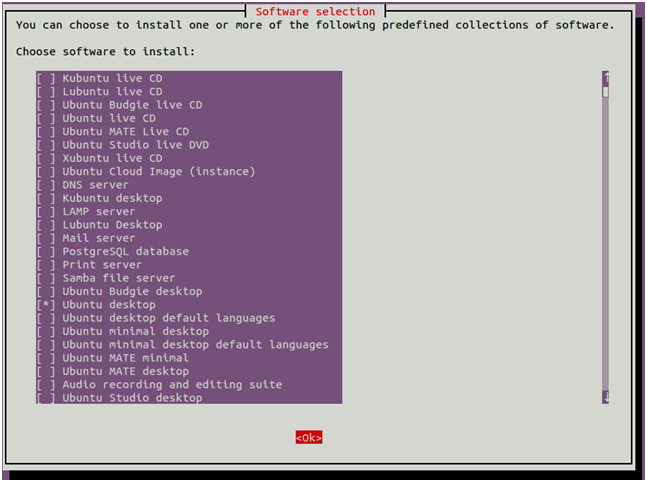
By default, Ubuntu Server does not include a Desktop Environment. TigerVNC server is designed to controls only desktop systems. So you will need to add a desktop environment in your server. First, update and upgrade all installed packages with the following command: Once your system is updated, install the tasksel utility to install a desktop environment: After installing Tasksel, launch the Tasksel utility with the following command: You should see the following interface:
Use the arrow key to scroll down the list and find Ubuntu desktop. Next, press the Space key to select it then press the Tab key to select OK then hit Enter to install the Ubuntu desktop. Once all the packages are installed, you will need to set your system boots into the graphical target. You can set it with the following command: Next, restart your system to apply the changes.
Step 2 – Install VNC Server on Ubuntu 18.04
The default Ubuntu 18.04 apt repositories contains TigerVNC server package. You can install it by just running the following command: After installing TigerVNC, create a new user and set a VNC password for that user. First, create a new user named tecadmin with the following command: Next, switch the user to tecadmin and set a VNC password with the following command: Provide your desired password as shown below: Next, start the VNC server using the following command: Once the VNC server is started, you should get the following output: You can verify your running VNC server using the following command: You should get the following output:
Step 2 – Installing VNC Client
In this section, we will install the RealVNC VNC client on the remote machine and connect to the VNC server. You can download the RealVNC client from the RealVNC download page. Make sure to select correct system architecture. Default page downloads 32bit package. Once the download is completed, install the downloaded package with the following command: Next, launch the VNC client from the Gnome application menu. Then, Click on the File menu => New connection to create a new connection. You should see the following screen:
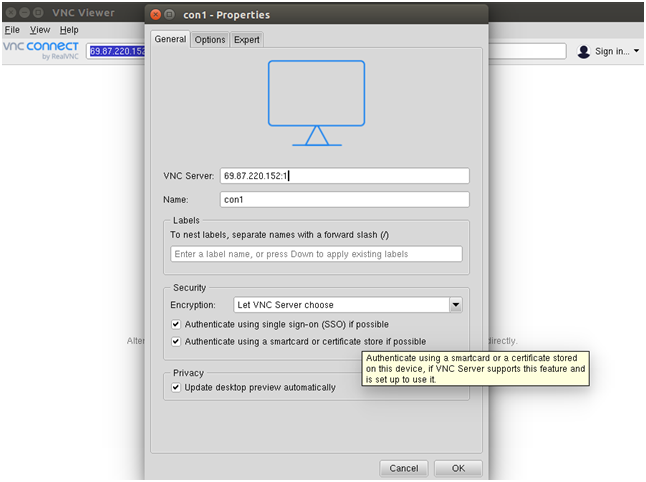
Provide the Name and IP address along with VNC session ID :1 of your VNC server and click on the OK to save the connection. You should see your saved connection in the following screen:
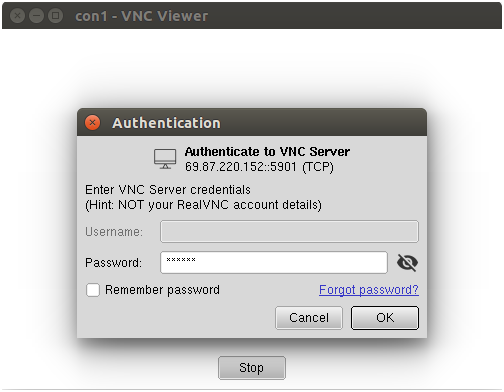
Now, double click on your newly created connection. You will be asked to provide your VNC password as shown below:
Provide your VNC password and click on the OK. Once connected, you should see your Ubuntu desktop screen:
Step 3 – Setup VNC for Your Desktop Environment
Before starting, stop the VNC instance using the vncserver command with a -kill option and the server session ID as an argument. You should get the following output: Killing Xtigervnc process ID 1719… success! Next, you will need to configure TigerVNC to work with Gnome. You can do it by creating new file xstartup inside .vnc directory: Add the following lines:
Save and close the file when you are finished. The above script will be executed automatically whenever you start or restart the TigerVNC server. Next, give execute permissions to the ~/.vnc/xstartup file:
Step 5 – Create a Systemd Service File for VNC
Next, you will need to create a systemd file for TigerVNC to manage the VNC service. You can create it with the following command: Add the following lines: Save and close the file then reload the systemd daemon with the following command: Next, enable the VNC service to start at system reboot with the following command: Next, start the VNC service with the following command:
Conclusion
Congratulations! you have successfully installed and setup the VNC server on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS Linux system. You can now connect Ubuntu Desktop from remote system using vnc viewer.